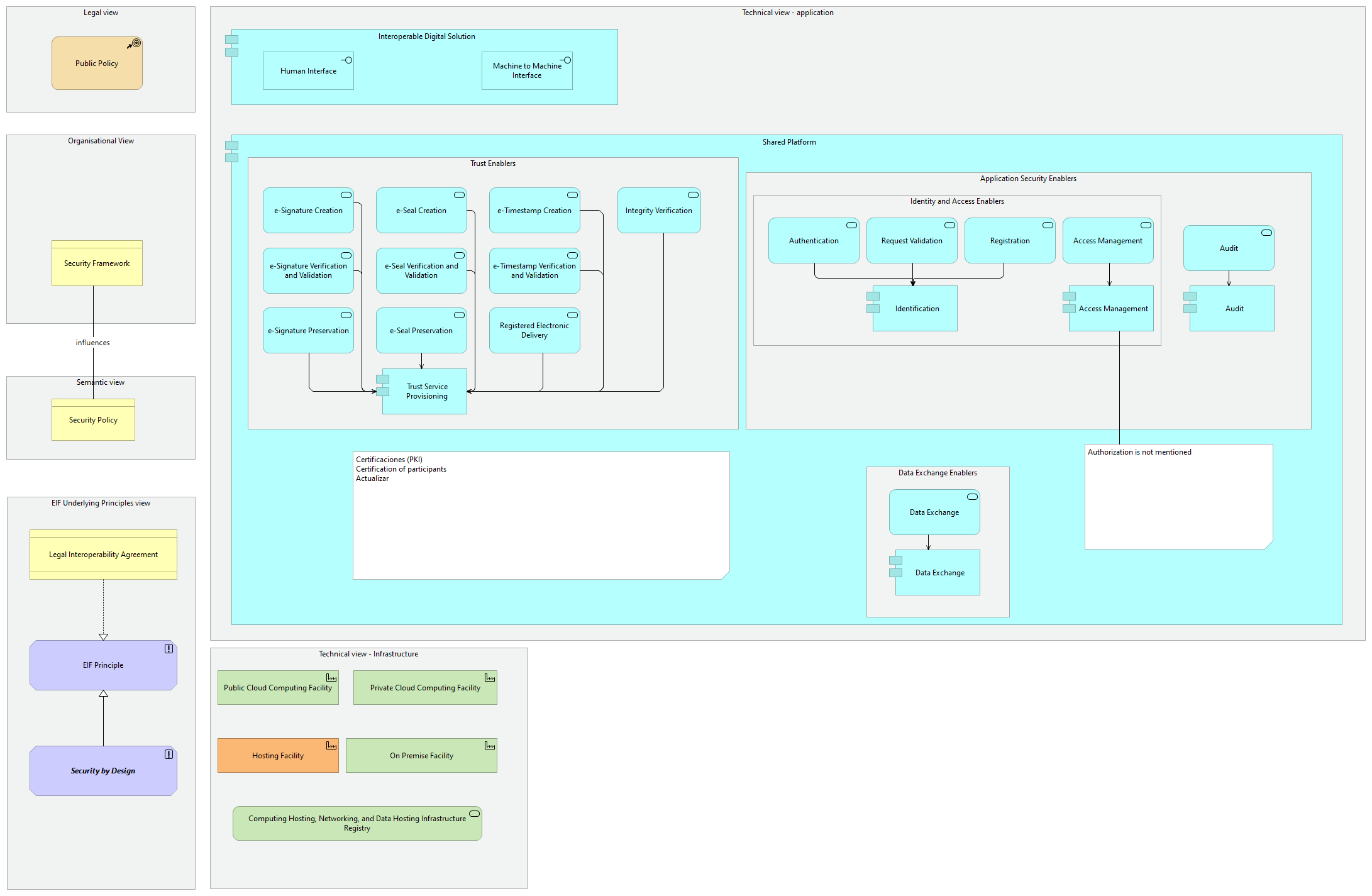
The Interoperability Security and Privacy viewpoint models the most salient Architecture Building Blocks related to both security and privacy in the domain of interoperability. Citizens and businesses must be confident that when they interact with public authorities they are doing so in a secure and trustworthy environment and in full compliance with relevant regulations, e.g. the Regulation and Directive on data protection, and the Regulation on electronic identification and trust services. Public administrations must guarantee the citizens’ privacy, and the confidentiality, authenticity, integrity and non-repudiation of information provided by citizens and businesses.
Security and privacy are primary concerns in the provision of public services. When public administrations and other entities exchange official information, the information should be transferred, depending on security requirements, via a secure, harmonised, managed and controlled network. Transfer mechanisms should facilitate information exchanges between administrations, businesses and citizens. Appropriate mechanisms should allow secure exchange of electronically verified messages, records, forms and other kinds of information between the different systems; should handle specific security requirements and electronic identification and trust services such as electronic signatures/seals creation and verification; and should monitor traffic to detect intrusions, changes of data and other type of attacks.
Source: The New EIF
https://ec.europa.eu/isa2/sites/isa/files/eif_brochure_final.pdf
Narrative: This viewpoint selects Architecture Building Blocks from the five different view highlighting the Security and Privacy aspects of the EIRA©:
1. The selected Architecture Building Block of the legal view shows the [Public Policy], which is that mainspring of the solution
2. The selected Architecture Building Block of the organisational view shows the [Security Framework], associated with the [Security Governance] which is that mainspring of the solution.
3. The selected Architecture Building Block of the semantic view shows the [Security Policy], which is that mainspring of the solution.
4. The selected Architecture Building Blocks of the technical view Application shows that a [Interoperable Digital Solution], which considers [Human Interface] and [Machine to Machine Interface] is supported by a [Shared platform] which uses [Trust Enablers], [Application Security Enablers], [Identification and Access Enablers] and [Data Exchange Enablers]. [Trust Enablers] such as [Integrity Verification Service], [e-Signature Creation Service], [e-Seal Creation Service], [e-Timestamp Creation Service], [e-Signature Verification and Validation Service], [e-Seal Verification and Validation Service], [e-Timestamp Verification and Validation Service], [e-Signature Preservation Service], [e-Seal Preservation Service] and [Registered Electronic Delivery Service], are all realised by a [Trust Service Provisioning Component]. [Identification and Access Enablers] is composed of [Authentication Service], [Request Validation Service] and [Registration Service] which are realised by [Identification Component] and that provides access to the [Directory], accessed also by the [Access Management Service], realised by the [Access Management Component]. [Application Security Enablers] is realised of [Firewall Service], composed of [Firewall Component] and [Audit Service], which is realised by an [Audit Component]. [Data Exchange Enablers] composed of Data Exchange Service] realised by the [Data Exchange Component].
5. The selected Architecture Building Blocks of the technical view Infrastructure shows an [Outsourcing Facility] and [On - Premise Facility] composed of [Back End Firewall] and [Extranet Firewall].
5. The selected Architecture Building Blocks of the EIF Underlying Principles view show that [Interoperability Specifications] realises [EIF Principles], the general intended properties used to achieve interoperability, of which the [Security and Privacy] is a specialisation. The interoperability Specifications can be used to define the interoperability aspects for any of the Architecture Building Blocks
.
| dct:title | Interoperability Security and Privacy viewpoint |