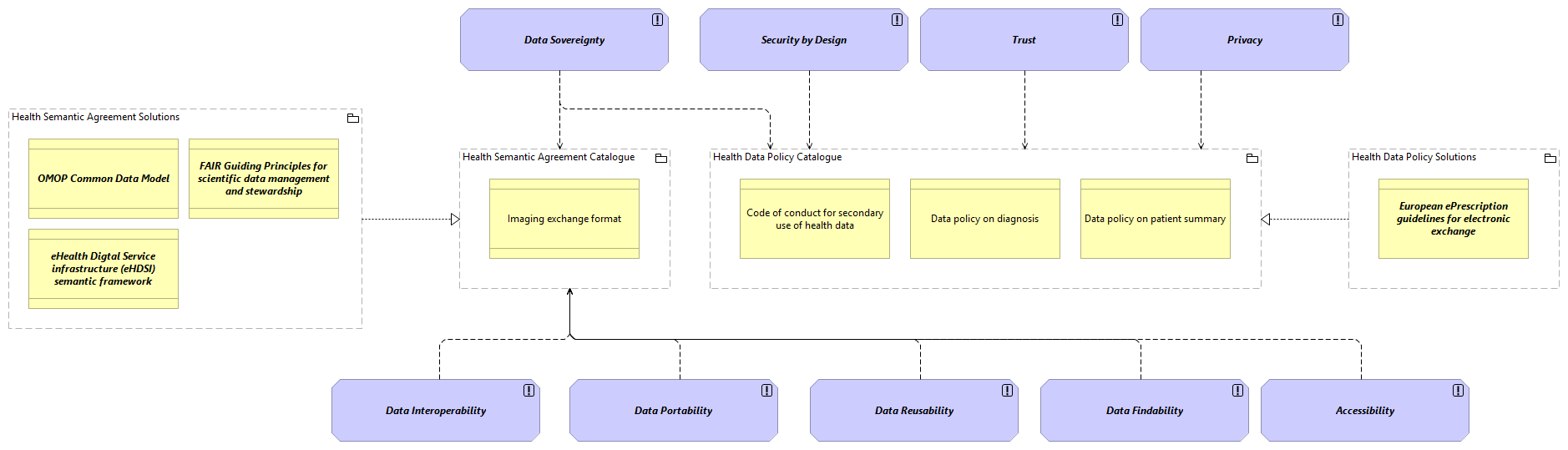
NARRATIVE:
The SV-Health Governance Architecture Principles view extends the Semantic view and provides a comprehensive framework for leveraging governance principles in the healthcare domain. It consists of several elements and their relationships, as described below:
1. Health Semantic Agreement Catalogue (Grouping ABB):
- Description: This element represents a catalog of semantic agreements related to healthcare.
- Elements:
- Imaging exchange format (Contract ABB):
- Description: This semantic agreement defines the methods and format for sharing medical images between national and European public administrations.
2. Health Data Policy Catalogue (Grouping ABB):
- Description: This element represents a catalog of data policies related to healthcare.
- Elements:
- Code of conduct for secondary use of health data (Business Object ABB):
- Description: This data policy defines the code of conduct for Member States in managing and processing genetic, biometric, or health data for research or statistical purposes.
- Data policy on diagnosis (Business Object ABB):
- Description: This data policy defines the rules and guidelines for the definition of databases related to Diagnosis.
- Data policy on patient summary (Business Object ABB):
- Description: This data policy defines the rules and guidelines for the definition of databases related to Patient Summary.
3. Security by Design (Principle SBB):
- Description: This principle emphasizes the importance of incorporating security measures into the design of healthcare systems.
4. Trust (Principle SBB):
- Description: This principle highlights the need for establishing trust in the healthcare ecosystem, ensuring the reliability and integrity of data and systems.
5. Privacy (Principle SBB):
- Description: This principle focuses on protecting the privacy of individuals' health data and ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.
6. Data Interoperability (Principle SBB):
- Description: This principle promotes the seamless exchange and interoperability of healthcare data across different systems and organizations.
7. Data Reusability (Principle SBB):
- Description: This principle encourages the design of healthcare data in a way that enables its reuse for various purposes, such as research and analytics.
8. Data Portability (Principle SBB):
- Description: This principle emphasizes the ability to transfer healthcare data between different systems and platforms, ensuring data portability.
9. Data Sovereignty (Principle SBB):
- Description: This principle asserts the control and ownership of healthcare data by the respective data owners, ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
10. Data Findability (Principle SBB):
- Description: This principle focuses on making healthcare data easily discoverable and accessible to authorized users.
11. Accessibility (Principle SBB):
- Description: This principle emphasizes the importance of ensuring equal access to healthcare data and services for all individuals.
12. Health Data Policy Solutions (Grouping ABB):
- Description: This element represents a collection of solutions related to health data policies.
- Elements:
- European ePrescription guidelines for electronic exchange (Business Object SBB):
- Description: These guidelines support Member States in developing the interoperability of ePrescriptions.
13. Health Semantic Agreement Solutions (Grouping ABB):
- Description: This element represents a collection of solutions related to health semantic agreements.
- Elements:
- OMOP Common Data Model (Contract SBB):
- Description: This semantic agreement allows for the systematic analysis of disparate observational databases.
- FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship (Contract SBB):
- Description: This semantic agreement defines the standards and guidelines for the management of data, enabling computational systems to find, access, interoperate, and reuse data with minimal human intervention.
- eHealth Digital Service Infrastructure (eHDSI) semantic framework (Contract SBB):
- Description: This semantic agreement represents the framework for cross-border health data exchange, enabling healthcare semantic experts to co-create and evolve crucial assets for semantic interoperability in cross-border eHealth services.
These elements and their relationships form the SV-Health Governance Architecture Principles view, which provides a structured approach to governance in the healthcare domain, ensuring the alignment of principles, policies, and solutions for effective and secure healthcare data management and interoperability.