NARRATIVE:
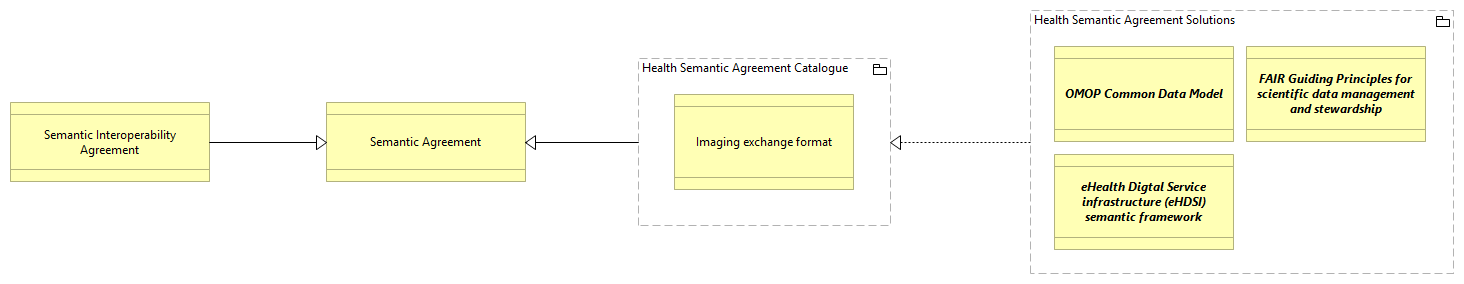
The SV-Health Semantic Agreements Catalogue view extends the Semantic view and provides a comprehensive framework for leveraging semantic agreements in the health domain. It consists of several elements and their relationships, as described below:
1. Semantic Agreement (Contract ABB):
- Description: Semantic Agreement ABB is a Contract formalizing an agreement from a peer to the common ontology. It is the result of a matching or mapping process used to resolve semantic discrepancies. The matching process includes linguistic base, internal, and external structure comparison. The agreement unit is developed as a component of the agreement.
- Motivation: The Semantic Agreement aims to ensure that peers in the health domain have a common understanding of the schema/ontology, labels, and the meaning of concepts. It eliminates semantic discrepancies and promotes interoperability.
2. Semantic Interoperability Agreement (Contract ABB):
- Description: Semantic interoperability agreement ABB is a Contract formalizing governance rules enabling collaboration between digital public services with ontological value.
- Motivation: The Semantic Interoperability Agreement establishes governance rules to facilitate collaboration between digital public services in the health domain. It ensures that ontological value is preserved and promotes interoperability.
3. Health Semantic Agreement Catalogue (Grouping ABB):
- Description: Health Semantic Agreement Catalogue is a grouping element.
- Motivation: The Health Semantic Agreement Catalogue serves as a catalog of semantic agreements specifically related to the health domain.
- Imaging exchange format (Contract ABB):
- Description: Semantic agreement between public administrations (national and European) defining the methods and format for sharing medical images.
- Motivation: The Imaging exchange format agreement defines the standards and guidelines for sharing medical images among public administrations. It ensures consistency and interoperability in image exchange.
4. Health Semantic Agreement Solutions (Grouping ABB):
- Description: Health Semantic Agreement Solutions is a grouping element.
- Motivation: The Health Semantic Agreement Solutions serve as a collection of semantic agreements that provide solutions in the health domain.
- OMOP Common Data Model (Contract SBB):
- Description: The OMOP Common Data Model allows for the systematic analysis of disparate observational databases.
- Motivation: The OMOP Common Data Model agreement enables the systematic analysis of different observational databases in the health domain. It promotes data interoperability and analysis.
- FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship (Contract SBB):
- Description: Semantic agreement defining the standards and guidelines on the management of data, ensuring computational systems can find, access, interoperate, and reuse data with minimal human intervention.
- Motivation: The FAIR Guiding Principles agreement ensures that scientific data in the health domain is managed according to standards and guidelines. It promotes data discoverability, accessibility, interoperability, and reusability.
- eHealth Digital Service Infrastructure (eHDSI) semantic framework (Contract SBB):
- Description: The eHealth Digital Service Infrastructure (eHDSI or eHealth DSI) is the initial deployment and operation of services for cross-border health data exchange. The semantic framework enables healthcare semantic experts to co-create and evolve crucial assets for semantic interoperability in cross-border eHealth services.
- Motivation: The eHealth Digital Service Infrastructure agreement establishes a semantic framework for cross-border health data exchange. It allows healthcare semantic experts to collaborate and develop foundational elements for semantic interoperability in eHealth services.
Overall, the SV-Health Semantic Agreements Catalogue view provides a structured representation of various semantic agreements and their relationships in the health domain. It aims to promote interoperability, resolve semantic discrepancies, and enable collaboration between digital public services.