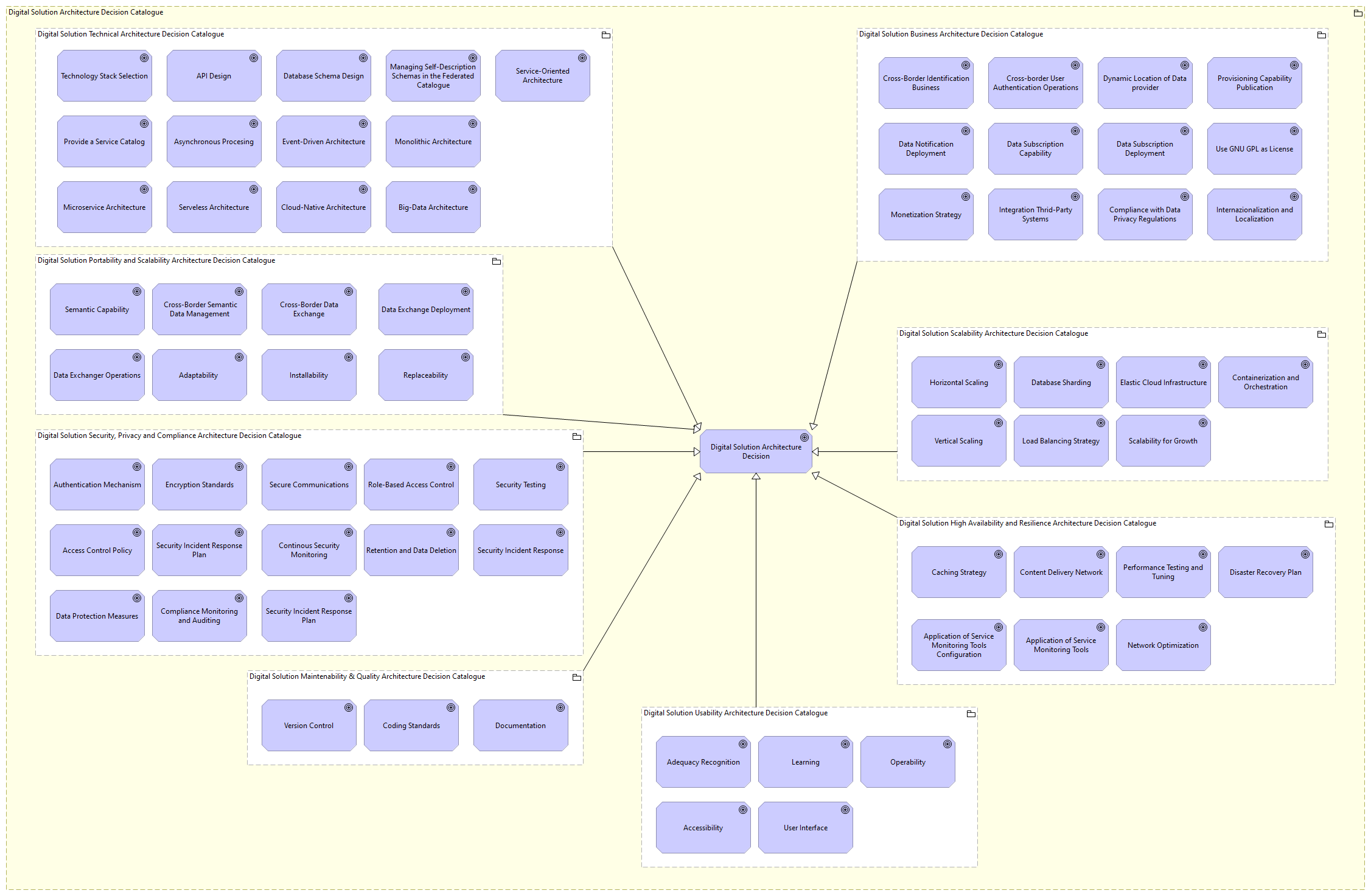
The IT Architecture Decision Records (ADRs) catalogue of a digital solution refers to a collection of documents that capture and document important architectural decisions made during the development and evolution of the solution.
These records serve as a valuable reference for the project team, stakeholders, and future developers, providing insights into the rationale behind key design choices and the impact of those decisions.
The ADR catalogue typically includes the following elements:
+ Title/Identifier: Each ADR is assigned a unique title or identifier to enable easy identification and retrieval.
+ Context: This section provides a brief overview of the background and context that led to the architectural decision. It may include factors such as business requirements, technical constraints, or market considerations.
+ Decision: This section outlines the specific decision made, describing the chosen solution or approach in detail. It should clearly articulate the problem being addressed and the solution chosen.
+ Alternatives Considered: It is essential to document alternative solutions or approaches that were evaluated before settling on the chosen decision. This helps to understand the reasoning behind the selected option.
+ Rationale: The rationale section explains the reasoning behind the decision. It may include factors such as performance, scalability, security, cost, maintainability, compatibility, or other relevant considerations.
+ Implications: This section discusses the potential impact of the decision on the system, including any anticipated benefits, drawbacks, risks, or dependencies introduced by the chosen approach.
+ Related ADRs: If the decision has dependencies or relationships with other ADRs, those connections should be documented in this section. It helps in establishing the traceability and understanding the interconnectedness of decisions.
+ Status and Date: Each ADR should include the current status (e.g., proposed, accepted, rejected, superseded) and the date when the decision was made or recorded.
By maintaining a comprehensive ADR catalogue, organizations can foster transparency, facilitate collaboration, and ensure consistency in architectural decision-making across teams and projects.
It serves as a knowledge repository and assists in understanding the evolution and reasoning behind the architecture of a digital solution.